Performance analysis
GPGPU acceleration of mathematical problems centers around runtime performance. Enhancing the performance of a software routine becomes easier if certain basic concepts about computer hardware are familiar. The best performance can only be acchieved if the (machine) code is tailord towards the hardware on which the code will be executed.
Basic hardware concepts, and a couple of more advanced ones, will be discussed using a few examples.
Dual socket, quad GPU compute node
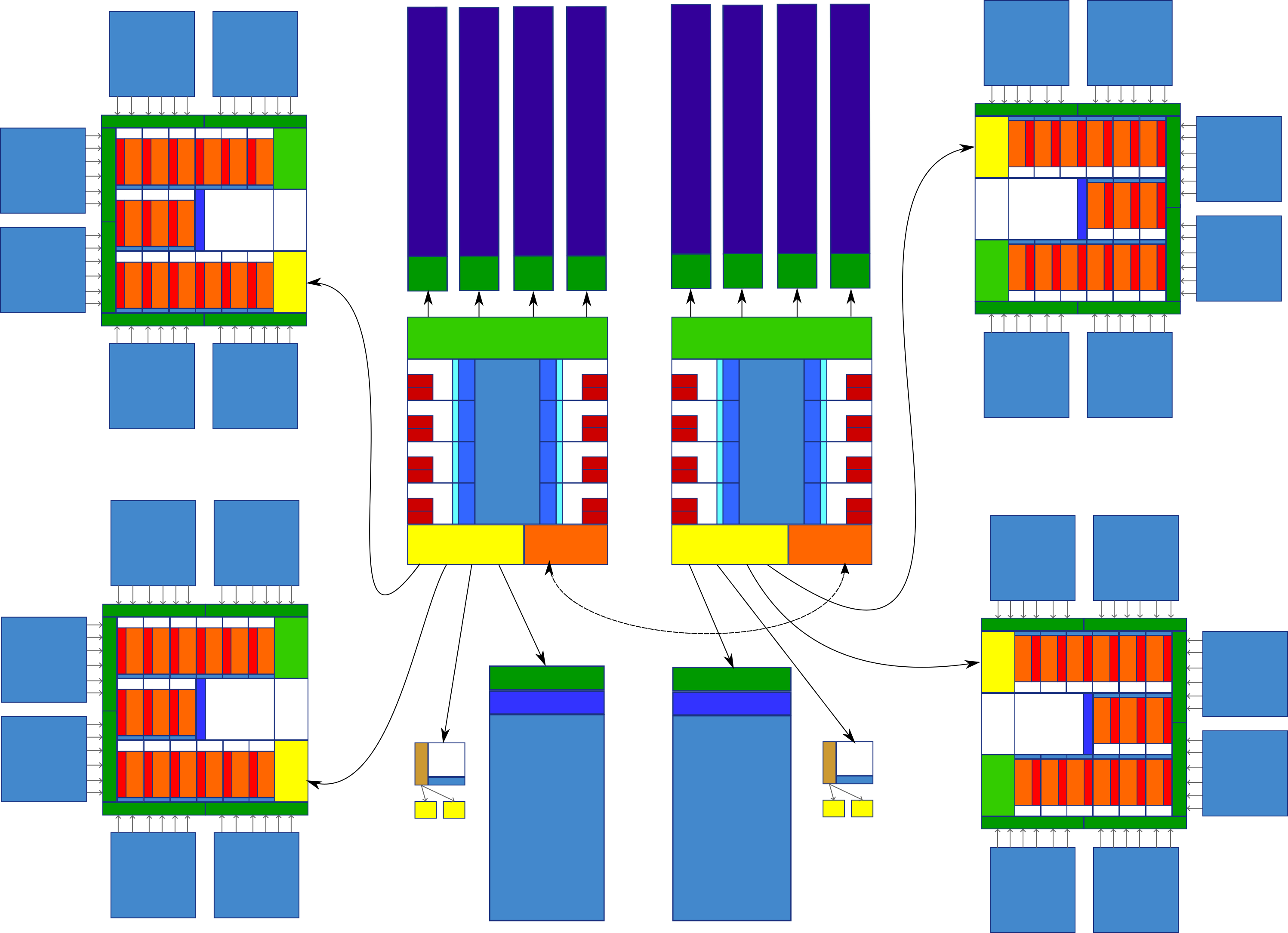
A high level block diagram of a dual socket, quad GPU, compute optimized rack server from around 2014/2015. The two CPUs (Central Processing Units) are Intel Xeon units from the Haswell/Broadwell generation. The four GPUs (Graphics processing unit) are NVIDIA Tesla K40 units, from the Kepler generation.
This specific example was chosen because it uses some of the first hardware that was really targeted at (double precision) High Perfomance Computing (HPC), contains enough complexity to accurately represent typical GPGPU compute nodes, but stil resembles consumer hardware at the fundamental levels.
Intel Xeon Gold 1632
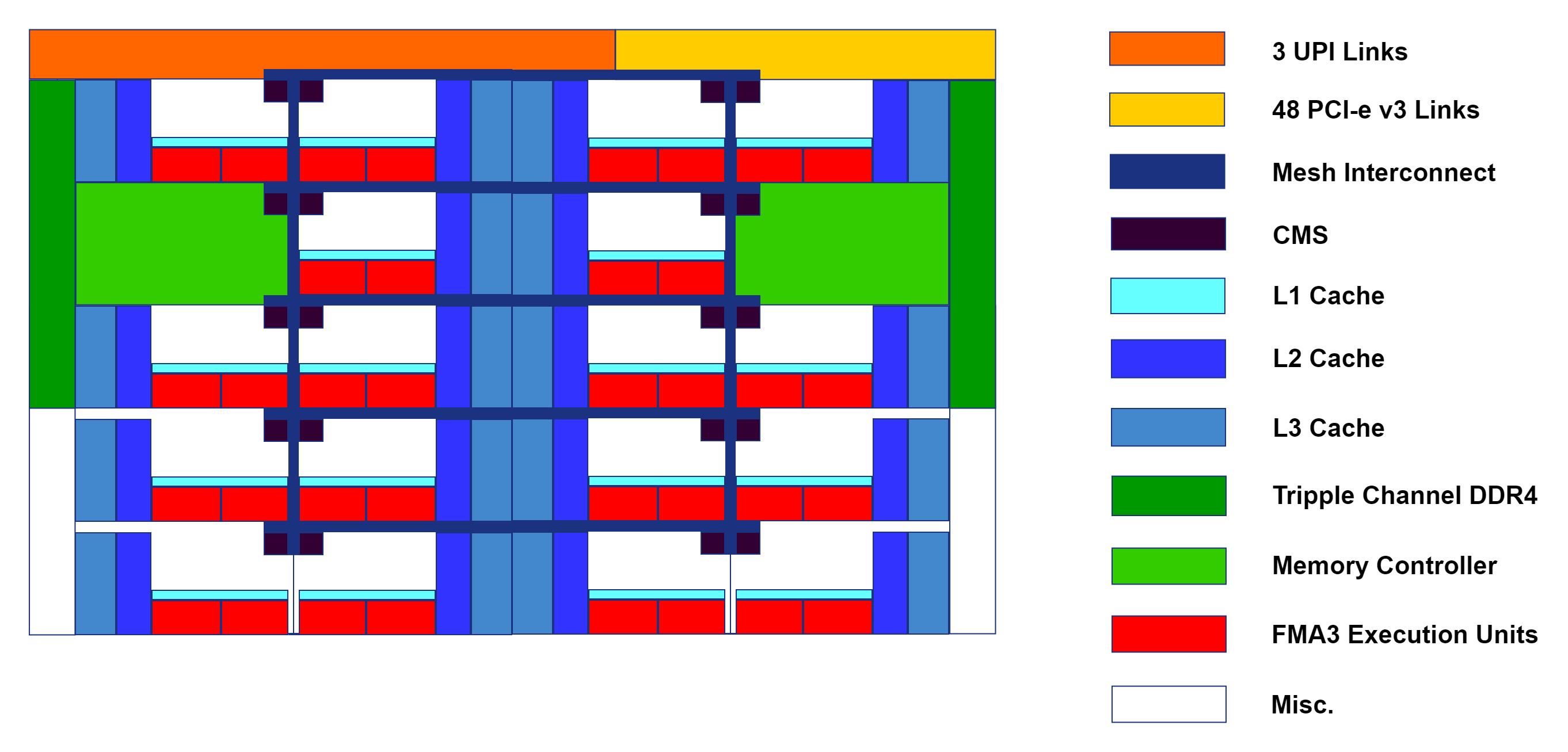
This example CPU is the Intel Xeon Gold 1632.
It contains:
- 14 cores and 28 threads
- 6 channel DDR4 ECC memory controller
- 19.25 MiB L3 cache
- 14 MiB (1 MiB/c) L2 cache
- 0.875 MiB (64 KiB/c) L1 cache
- 48 PCI-e v3.0 lanes
- 2 AVX-512 FMA units per core